Project 8 - Gold Price Prediction using Machine Learning with Python
My Machine Learning Beginner Projects, Entry 8
I am Salim Olanrewaju Oyinlola. I identify as a Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence enthusiast who is quite fond of making use of data and patterns to develop insights and analysis.
In my opinion, Machine learning is where the computational and algorithmic skills of data science meets the statistical thinking of data science. The result is a collection of approaches that requires effective theory as much as effective computation. There are a plethora of machine learning model, with each of them working best for different problems. As such, I believe understanding the problem setting in machine learning is essential to using these tools effectively. Now, the best way to UNDERSTAND different problem settings is by PLAYING AROUND with different problem settings. That is the genesis behind this writing series - My Machine Learning Projects. Over the course of this writing series, I would solve a machine learning problem daily. These problems will range from a plethora of fields whilst requiring and covering a range of models. A link to my previous articles can be found here.
Project Description: This project is a regression used to predict the prices of gold using certain properties attributed with the gold sample.
URL to Dataset: Download here
Line-by-line explanation of Code
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn import metrics
import numpy as np imports the numpy library which can be used to perform a wide variety of mathematical operations on arrays.
import pandas as pd imports the pandas library which is used to analyze data.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt imports the PyPlot function from the MatPlotLib library which is used to visualize data and trends in the data.
import seaborn as sns imports the seaborn library which is used for making statistical graphics. It builds on top of matplotlib and integrates closely with pandas data structures. Seaborn helps you explore and understand your data.
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split imports the train_test_split function from sklearn's model_selection library. It will be used in spliting arrays or matrices into random train and test subsets.
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier imports the RandomForestClassifier ML model. The classsifier is an emsemble learner built on decision trees.
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score imports the accuracy_score function from sklearn's metrics library. This model is used to ascertain the performance of our model.
salim_gold_data = pd.read_csv(r'C:\Users\OYINLOLA SALIM O\Downloads\gld_price_data.csv')
This line of code loads the csv data to a Pandas DataFrame.
salim_gold_data.tail()
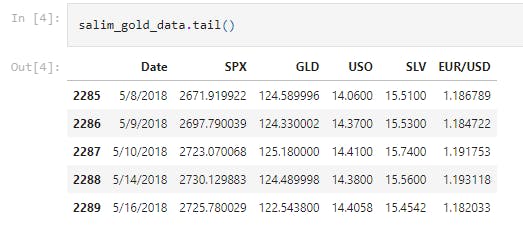
This line of code prints the last 5 rows of the dataframe. This performs the same function the salim_gold_data.head() would have performed but I chose to use spice things up a little this time.
salim_gold_data.shape
This displays the number of rows and columns.
salim_gold_data.isnull().sum()
This checks the number of missing values in the dataset. It is seen that there is no missing values in the dataset.
salim_gold_data.describe()
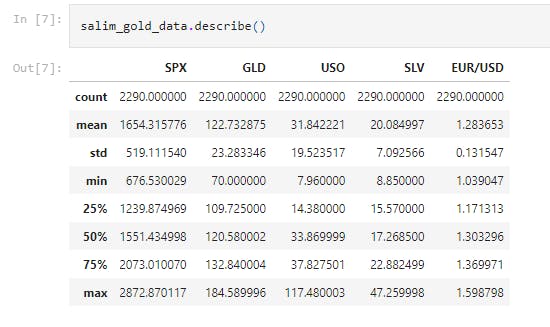
This displays the statistical measure of the data (i.e. the mean, median, max, min 25th, 50th, 75th percentile values etc.)
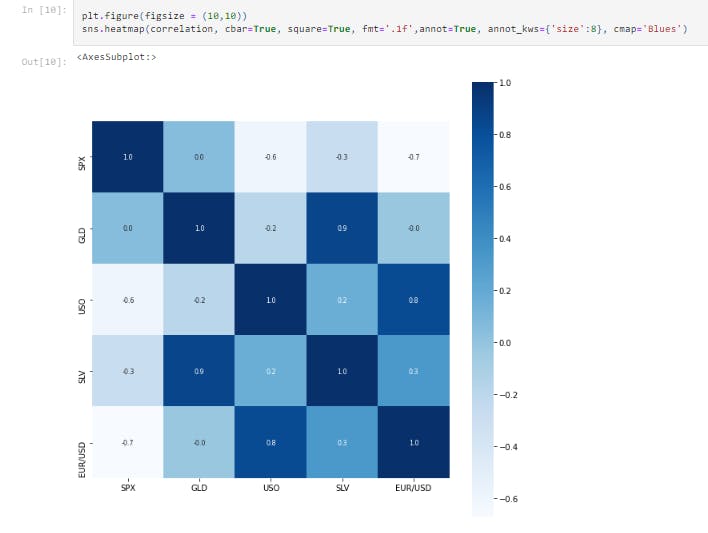
correlation = salim_gold_data.corr()
This creates an instance of the correlation function. It is important to note that correlation can be divided as follows; i. Positive Correlation ii. Negative Correlation
plt.figure(figsize = (10,10))
sns.heatmap(correlation, cbar=True, square=True, fmt='.1f',annot=True, annot_kws={'size':8}, cmap='Blues')
This constructs a heatmap to understand the correlation as shown below.
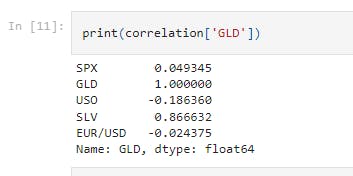
print(correlation['GLD'])
This display the correlation values of the attribute, GLD
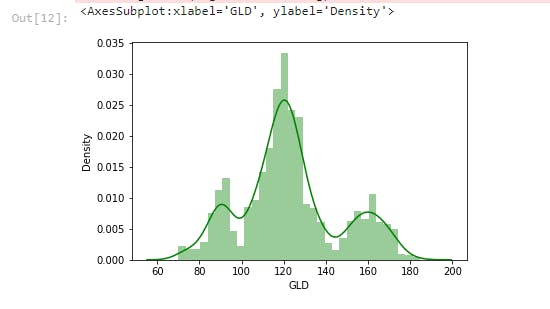
sns.distplot(salim_gold_data['GLD'],color='green')
This line of code checks the distribution of the GLD Price.
X = salim_gold_data.drop(['Date','GLD'],axis=1)
Y = salim_gold_data['GLD']
This block of code separates the data and Label.
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size = 0.2, random_state=2)
The train_test_split method that was used earlier is hence called and used to divide the dataset into train set and test set.
- The 0.2 value of test_size implies that 20% of the dataset is kept for testing whilst 80% is used to train the model.
regressor = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=100)
This line of code intializes an instance of the RandomForestRegressor Machine Learning training model. The n_estimators parameter indicates the number of trees in the forest.
regressor.fit(X_train,Y_train)
This line of code trains the model.
test_data_prediction = regressor.predict(X_test)
This predicts on the test data and saves the arrays of predictions in the variable, test_data_prediction.
error_score = metrics.r2_score(Y_test, test_data_prediction)
print("R squared error : ", error_score)
This evaluates the R-squared error. The error seen was 0.9887338861925125.
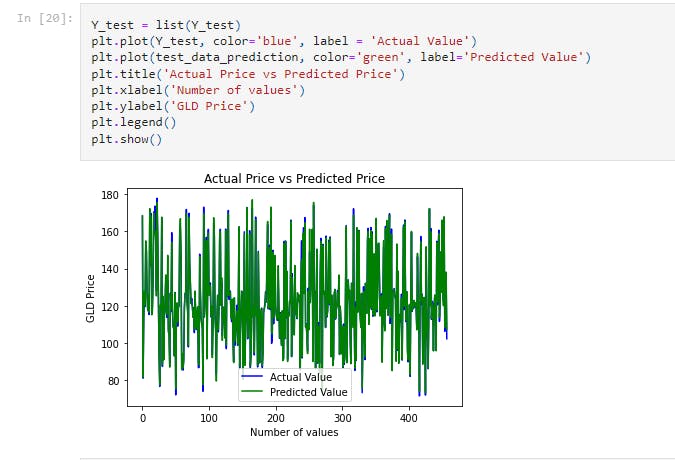
Y_test = list(Y_test)
plt.plot(Y_test, color='blue', label = 'Actual Value')
plt.plot(test_data_prediction, color='green', label='Predicted Value')
plt.title('Actual Price vs Predicted Price')
plt.xlabel('Number of values')
plt.ylabel('GLD Price')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
This plots a graph of the actual and predicted values of GLD price against the number of values.
That's it for this project. Be sure to like, share and keep the discussion going in the comment section. .ipynb file containing the full code can be found here.
