Project 4 - Fake News Prediction using Machine Learning with Python
My Machine Learning Beginner Projects, Entry 4
I am Salim Olanrewaju Oyinlola. I identify as a Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence enthusiast who is quite fond of making use of data and patterns to develop insights and analysis.
In my opinion, Machine learning is where the computational and algorithmic skills of data science meets the statistical thinking of data science. The result is a collection of approaches that requires effective theory as much as effective computation. There are a plethora of machine learning model, with each of them working best for different problems. As such, I believe understanding the problem setting in machine learning is essential to using these tools effectively. Now, the best way to UNDERSTAND different problem settings is by PLAYING AROUND with different problem settings. That is the genesis behind this writing series - My Machine Learning Projects. Over the course of this writing series, I would solve a machine learning problem daily. These problems will range from a plethora of fields whilst requiring and covering a range of models. A link to my previous articles can be found here.
Project Description: This model is capable of detecting if a given news headline is fake.
URL to Dataset: Download here
Line-by-line explanation of Code
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import re
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
from nltk.stem.porter import PorterStemmer
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
The block of codes above imports the dependencies used in the model.
import numpy as np imports the numpy library which can be used to perform a wide variety of mathematical operations on arrays.
import pandas as pd imports the pandas library which is used to analyze data.
import re imports the regular expression library which provides regular expression matching operations similar to those found in Perl. A regular expression (or RE) specifies a set of strings that matches it; the functions in this module let you check if a particular string matches a given regular expression (or if a given regular expression matches a particular string, which comes down to the same thing).
from nltk.corpus import stopwords imports a list of stop words using the corpus function in the nltk module which contains a list of stop words. The stopwords in nltk are the most common words in data. They are words that you do not want to use to describe the topic of your content.
from nltk.stem.porter import PorterStemmer imports the PorterStemmer function from the nltk.stem.porter module. Stemmers remove morphological affixes from words, leaving only the word stem.
- NOTE:
nltkstands for Natural Language Toolkit which is used for natural language processing with Python.
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer imports the TfidfVectorizer function from sklearn's feature_extraction module. This converts a collection of raw documents to a matrix of TF-IDF features.
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split imports the train_test_split function from sklearn's model_selection library. It will be used in spliting arrays or matrices into random train and test subsets.
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression imports the LogisticRegression Machine Learning model from sklearn's linear_model library. This model will be used in training the model.
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score imports the accuracy_score function from sklearn's metrics library. This model is used to ascertain the performance of our model.
- NOTE: The logistic regression model which is a classification model is used because the problem is a classification problem. We are trying to group texts into Fake news or real news based on certain properties.
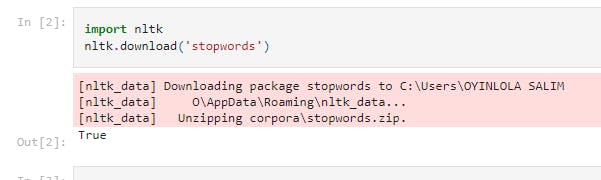
import nltk
nltk.download('stopwords')
This downloads every stopwords in nltk data, so this can take a while. It should return an output, True as shown below.
print(stopwords.words('english'))
This line of code prints the stopwords in English.
These words include: 'i', 'me', 'my', 'myself', 'we', 'our', 'ours', 'ourselves', 'you', "you're", "you've" etc.
salim_news_dataset = pd.read_csv(r'C:\Users\OYINLOLA SALIM O\Downloads\fake-news\train.csv')
This loads the dataset to a pandas DataFrame with the variable name, salim_news_dataset
salim_news_dataset.head()
This print the first 5 rows of the dataframe.
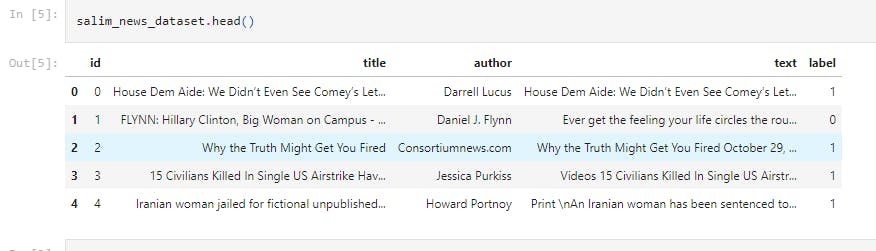
The attributes are as follows;
id: unique id for a news article
title: the title of a news article
author: author of the news article
text: the text of the article; could be incomplete
label: a label that marks whether the news article is real or fake:
1: Fake news
0: real News
salim_news_dataset.isnull().sum()
This counts the number of missing values in the dataset. It is seen that 558 missing values as title, 1957 missing in the author and 39 missing in text and no missing value in id and label.
salim_news_dataset = salim_news_dataset.fillna('')
This replaces the null values with empty string.
salim_news_dataset['content'] = salim_news_dataset['author']+' '+salim_news_dataset['title']
This merges the author name and news title.
X = salim_news_dataset.drop(columns='label', axis=1)
Y = salim_news_dataset['label']
This block of code separates the data & label.
salim_port_stem = PorterStemmer()
This creates an instance of PorterStemmer. Recall that Stemmers remove morphological affixes from words, leaving only the word stem.
def stemming(content):
stemmed_content = re.sub('[^a-zA-Z]',' ',content)
stemmed_content = stemmed_content.lower()
stemmed_content = stemmed_content.split()
stemmed_content = [salim_port_stem.stem(word) for word in stemmed_content if not word in stopwords.words('english')]
stemmed_content = ' '.join(stemmed_content)
return stemmed_content
This block of code creates a function that stems inputs. Stemming is the process of reducing a work to its root word. Removes the prefix, suffixes etc.
salim_news_dataset['content'] = salim_news_dataset['content'].apply(stemming)
This stems the inputs.
X = salim_news_dataset['content'].values
Y = salim_news_dataset['label'].values
This block of code separates the data and label.
Y.shape
This returns the number of Y values we have. Here, we have 20800.
vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer()
vectorizer.fit(X)
X = vectorizer.transform(X)
This converts the textual data into numerical data.
print(X)
This line of code is present just to ensure that we were able to transform the textual data into numerical data.
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size = 0.2, stratify=Y, random_state=2)
The train_test_split method that was used earlier is hence called and used to divide the dataset into train set and test set.
- The 0.2 value of test_size implies that 20% of the dataset is kept for testing whilst 80% is used to train the model.
model = LogisticRegression()
model.fit(X_train, Y_train)
This block of code creates an instance of the Logistic Regression classification ML model and trains it with the train set.
X_train_prediction = model.predict(X_train)
training_data_accuracy = accuracy_score(X_train_prediction, Y_train)
print('Accuracy score of the training data : ', training_data_accuracy)
This block of code evaluates the accuracy score on the training data. We see an accuracy score of 0.9866586538461538
X_test_prediction = model.predict(X_test)
test_data_accuracy = accuracy_score(X_test_prediction, Y_test)
print('Accuracy score of the test data : ', test_data_accuracy)
This block of code evaluates the accuracy score on the test data. We see an accuracy score of 0.9790865384615385
That's it for this project. Be sure to like, share and keep the discussion going in the comment section. .ipynb file containing the full code can be found here.
